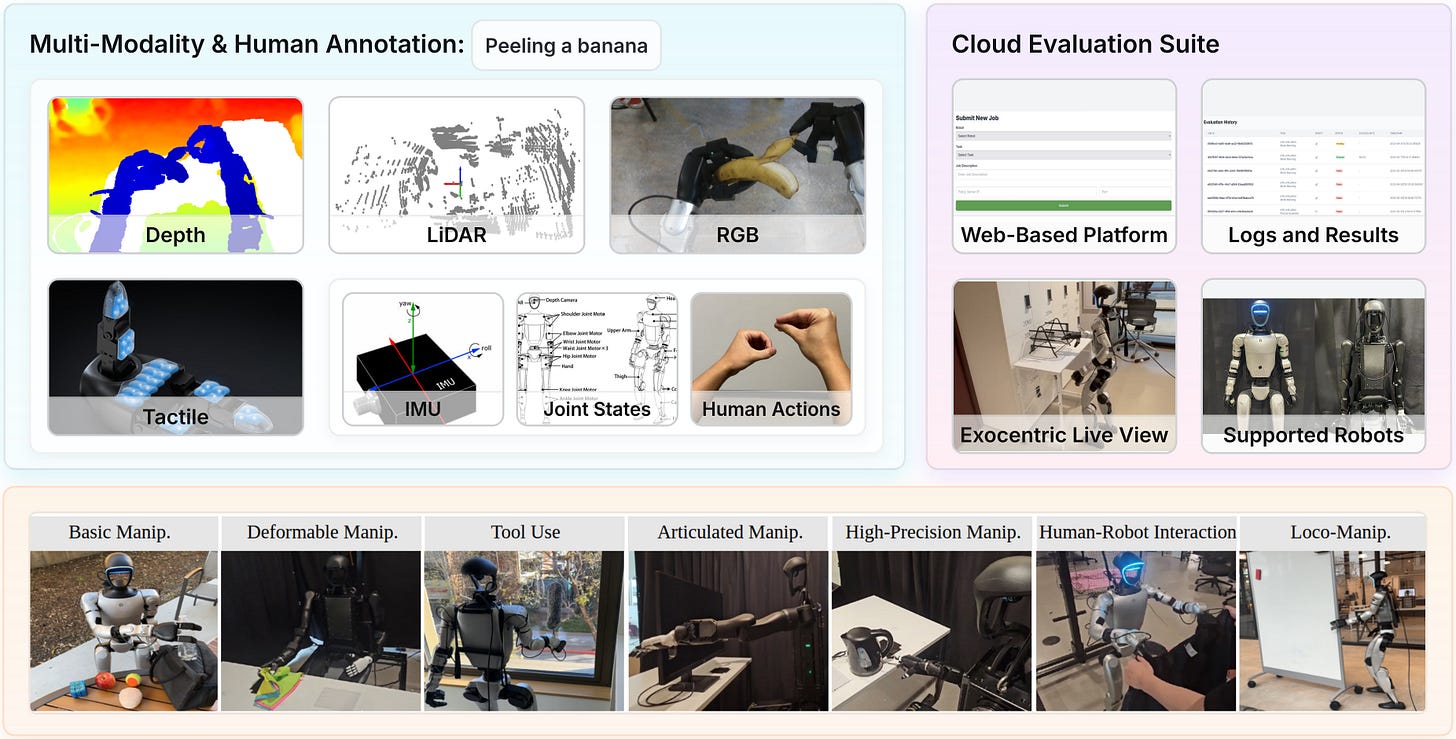
Robotics, as we know, has a data problem. Many workarounds have been proposed, but one of the most important things is just to collect a large amount of real-robot data — something very difficult, especially for mobile humanoids. Enter Humanoid Everyday, which provides a large, diverse dataset of humanoid mobile manipulation examples.
With 260 tasks across 7 different categories, this is the largest humanoid robot dataset we’ve ever seen — and, most importantly, the authors have provided clear evidence that it works for robot learning.
Zhenyu Zhao, Hongyi Jing, Xiawei Liu, Jiageng Mao, and Yue Wang all join us to tell us more about their thought process, their dataset, and the future of humanoid robot evaluation.
Watch Episode #51 of RoboPapers, with Michael Cho and Chris Paxton, now!
Abstract:
From loco-motion to dextrous manipulation, humanoid robots have made remarkable strides in demonstrating complex full-body capabilities. However, the majority of current robot learning datasets and benchmarks mainly focus on stationary robot arms, and the few existing humanoid datasets are either confined to fixed environments or limited in task diversity, often lacking human-humanoid interaction and lower-body locomotion. Moreover, there are a few standardized evaluation platforms for benchmarking learning-based policies on humanoid data. In this work, we present Humanoid Everyday, a large-scale and diverse humanoid manipulation dataset characterized by extensive task variety involving dextrous object manipulation, human-humanoid interaction, locomotion-integrated actions, and more. Leveraging a highly efficient human-supervised teleoperation pipeline, Humanoid Everyday aggregates high-quality multimodal sensory data, including RGB, depth, LiDAR, and tactile inputs, together with natural language annotations, comprising 10.3k trajectories and over 3 million frames of data across 260 tasks across 7 broad categories. In addition, we conduct an analysis of representative policy learning methods on our dataset, providing insights into their strengths and limitations across different task categories. For standardized evaluation, we introduce a cloud-based evaluation platform that allows researchers to seamlessly deploy their policies in our controlled setting and receive performance feedback. By releasing Humanoid Everyday along with our policy learning analysis and a standardized cloud-based evaluation platform, we intend to advance research in general-purpose humanoid manipulation and lay the groundwork for more capable and embodied robotic agents in real-world scenarios.